With studies suggesting that patients with COVID-19 who are deficient in vitamin D have poorer outcomes than those who have normal vitamin D levels, people are now asking how to pump up their levels of the important nutrient. But vitamin D has always been important to your health, as it’s essential for building bone and maintaining skeletal structure, promoting calcium absorption, aiding immune function, and helping to reduce inflammation. The challenge is finding it — it doesn’t naturally occur in many foods like other vitamins and minerals. Fortunately, there are plenty of easy ways to get the recommended dietary allowance of this necessary nutrient: 600 international units, or IU, each day.
Related: 11 Diet Supplements: Do You Really Need Them?
Going Outside

Getting out in the sun is perhaps the easiest way to boost vitamin D, which is created when ultraviolet B rays strike the skin. The best time is midday during the warmer months, when the sun’s rays are strongest. Keep in mind that glass blocks UVB, so sitting behind a window doesn’t work. Sitting outside for as little as 10 minutes is sufficient for many people. A host of other outdoor activities, including gardening, biking, and sports, are just as effective.
Related: 22 Tips to Keep Gardening Dirt Cheap
Fatty Fish

Fish are one of the few natural food sources of vitamin D, and fatty fish are the best bets. For example, a 3-ounce portion of rainbow trout boasts about 635 IU, according to the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s FoodData Central. The same size serving of Atlantic herring delivers about 140 IU of vitamin D, or about 30 percent of the recommended amount.
Related: 20 Recipes and Tips for Grilling Fish This Summer
Canned Fish

While fresh fish (particularly wild caught) typically contains more vitamin D than its canned counterparts, canned fish is still a good source of this essential nutrient. Three ounces of canned pink salmon supplies 479 IU of vitamin D, and a cup of sardines provides 288 IU.
Related: 27 Unusual Canned Foods You Might Actually Want to Eat
Cod Liver Oil

Cod liver oil is another excellent source of naturally occurring vitamin D, but the taste is unpalatable to many. Try some tips and tricks to help the medicine go down, such as mixing cod liver oil into homemade salad dressing or stirring it into yogurt. And if that doesn’t work, capsules containing cod liver oil are just as effective — and more convenient.
For more smart health and fitness tips, please sign up for our free newsletters.
Fortified Milk

Although dairy products aren’t a natural source of vitamin D, nearly all milk sold in the United States is fortified with about 100 IU of vitamin D in an 8-ounce serving. This applies to all types of milk — full-fat, 2 percent, 1 percent, and skim — but generally not milk products such as cheese and ice cream.
Related: 24 Organic Grocery Bargains From Aldi
Trending on Cheapism
Orange Juice

Likewise, vitamin D isn’t naturally present in oranges, but some brands of orange juice are fortified with varying amounts of vitamin D, along with calcium, as an alternative for those who don’t — or can’t — consume milk products. Think of it as juiced-up juice.
Related: 40 Breakfast Foods Ranked by Their Calorie Count
Mushrooms
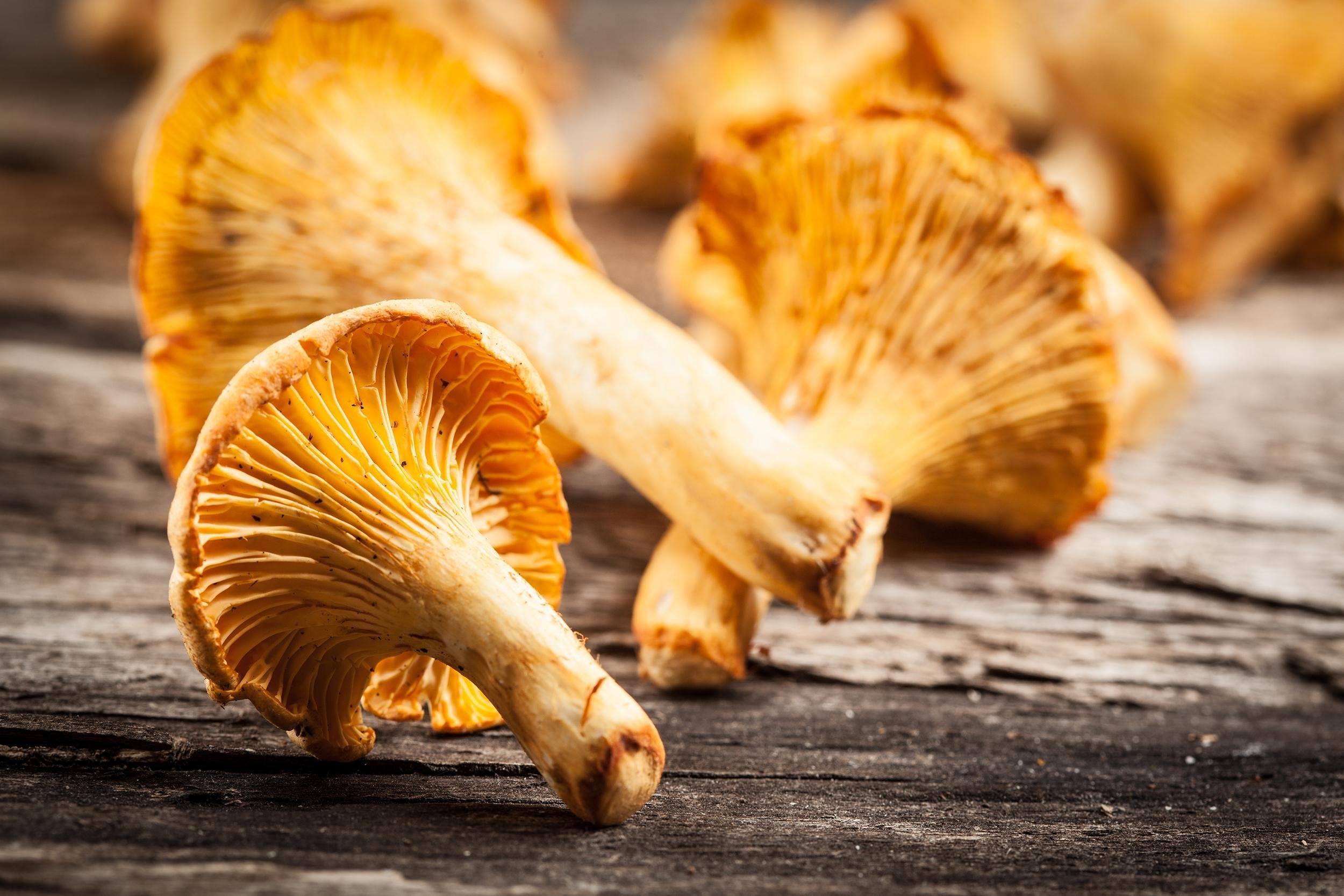

Some mushrooms, when exposed to sunlight (or UV light in general), produce and become a source of vitamin D for human consumption. Chanterelle mushrooms, in particular, are a good source: 1 cup can provide 114 IU of the nutrient. A cup of cooked shiitake mushrooms yields about 40 IU.
Related: 36 Foods You Wouldn’t Think to Grill But Should Definitely Try
Eggs

If you love eggs, good news — the yolk is home to about 40 IU of vitamin D. This is not a lot, but given that there simply aren’t a lot of natural sources of the vitamin, it’s good to know that eating the whole egg (not just the white) ups your daily allotment of this important nutrient.
Related: 13 Simple Ways to Cook Eggs
Sign up for our newsletter
Beef Liver

Three ounces of cooked beef liver supplies about the same amount of vitamin D found in an egg yolk — about 40 IU. You can’t rely on liver for a full complement of vitamin D, of course, but it helps to know that an occasional meal helps boost your daily intake.
Fortified Cereal

Many brands of ready-to-eat breakfast cereal contain added vitamin D, along with other vitamins and minerals. Fortified cereal alone isn’t a significant source of vitamin D — it supplies about 10 percent of the daily requirement. But adding milk raises the amount of vitamin D to 25 percent of the recommended amount. Note: Some non-GMO cereals aren’t fortified with vitamin D, likely due to the difficulty of sourcing vitamins from non-genetically modified sources.
Related: 30 Things You Didn’t Know About Your Favorite Childhood Cereals
Supplements

While vitamin supplements can be expensive, vitamin D can be bought cheaply. A 600-count bottle of Kirkland Signature vitamin D3 softgels from Costco with 2,000 IU (about half the upper limit for adults, according to the National Institutes of Health) costs about $13, or a little over 2 cents a tablet. Big-box retailers such as Walmart and Target offer similarly priced products — but be sure to compare the dosage, which can vary considerably from product to product.